Our colleague, Gabriel Văsii, Junior Engineer, presents the impact of VPN
solutions based on MPLS on data networks, explaining the technology and its benefits. Through
practical VPN configuration examples, he illustrates how MPLS networks allow companies to
efficiently transmit data and create secure private networks for clients, providing a more stable and
high-performing foundation for their digital operations.

In a world that’s increasingly interconnected, organizations need to ensure that their networks are not only fast, but also secure and scalable. MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) stands out as one of the leading solutions that addresses these needs. Recently, I had the opportunity to dive deep into this technology through implementing VPN solutions based on MPLS and BGP, helping me understand not just the power of this technology, but also its significance in today’s network landscape.
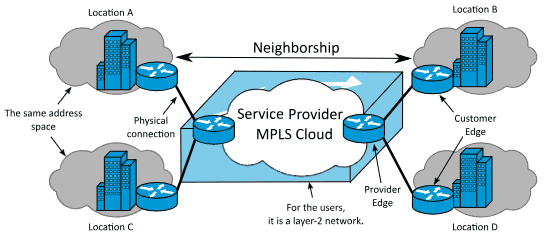
What is MPLS and why is it so important?
At its core, MPLS is a routing technology that enables efficient data packet transmission across a network using “labels.” Unlike traditional routing, which relies on IP addresses, MPLS directs data packets based on these labels, significantly reducing processing time and optimizing data flow. This is essential for applications requiring low latency and high availability, such as IP telephony or video streaming.
One of MPLS’s greatest strengths is its flexibility. The technology is not restricted to a specific type of traffic or protocol, making it ideal for networks to handle a variety of services. Additionally, MPLS allows service providers to offer a wide range of network services, such as VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), QoS (Quality of Service), and more, all on the same infrastructure.
How does MPLS work?
MPLS works by assigning a label to each data packet upon entering an MPLS network. This label contains information about the path the packet should follow through the network, enabling it to be quickly switched from node to node without requiring a detailed IP address inspection at every step. This label-based switching process is what makes MPLS significantly faster than traditional routing methods.
In a project I recently worked on, I configured protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) to establish and manage routing paths within the network. For instance, OSPF was used to ensure rapid route convergence within the service provider’s network, while LDP distributed the essential routing labels required for MPLS functionality.
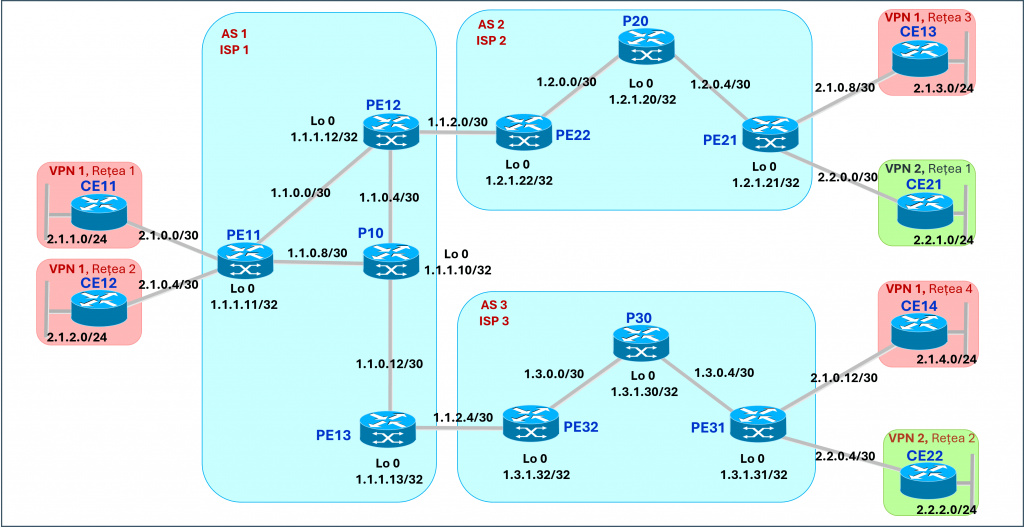
MPLS VPN topology with three providers
MPLS and VPNs: a powerful combination
One of the most important applications of MPLS is in creating VPNs (Virtual Private Networks). By using VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding), MPLS allows multiple routing instances to coexist on the same physical infrastructure. This means that each client (in the case of a Service Provider) or department within a single client organization can have its own private network, completely isolated from others, with unique routing rules and security policies.
For example, we can set up two separate VPNs for two different clients. Each VPN would have its own routes and security policies, managed through VRFs on the Provider Edge (PE) routers. This not only ensures data confidentiality for each client but also allows for centralized and efficient network management, even with shared infrastructure.
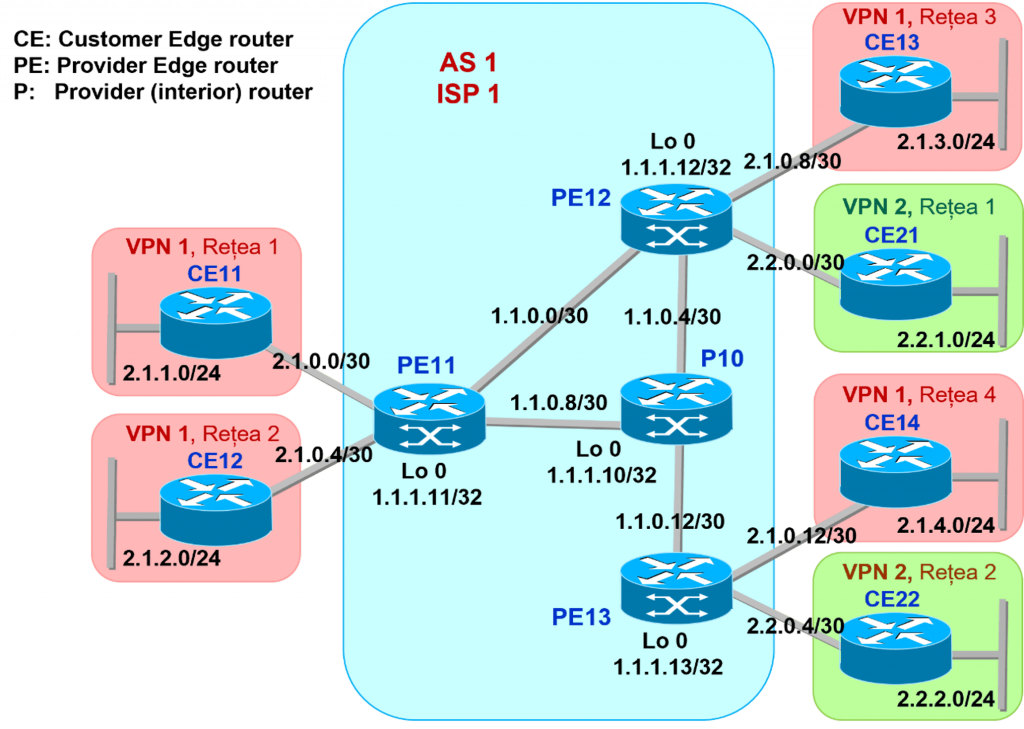
MPLS VPN topology with a single provider
Integration with BGP
Another crucial component in MPLS implementation is integration with the BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). BGP is used to manage routes between different autonomous systems (ASes), and in the MPLS context, its extended version, MP-BGP (Multiprotocol BGP), enables the transport of not only IPv4 routes but also VPNv4 routes. This functionality is essential to ensure that VPN traffic is routed correctly across the MPLS network. MP-BGP is configured to transport routes between different client sites, making sure each data packet reaches the right destination, regardless of the complexity of the provider’s network. BGP also plays an important role in preventing routing loops and ensuring redundancy, both of which are crucial in large-scale networks.
The practical benefits of MPLS
After going through the stages of implementation and configuration, I realized the power of this technology. Essentially, MPLS provides a solution that not only simplifies the routing process but also significantly enhances network performance. Scalability is another major advantage: as an organization grows, MPLS can be easily expanded to accommodate new locations and users without compromising security or performance.
Another significant benefit of MPLS is enhanced security. Additionally, by using encryption technologies, such as IPsec, to protect data, MPLS becomes even more attractive for organizations handling sensitive information.
MPLS is not just a networking technology; it’s a game-changer for companies looking to improve the performance, security, and scalability of their networks. While its implementation may seem complex initially, the long-term benefits make the effort well worth it. With its unique combination of speed, flexibility, and security, MPLS is undoubtedly the solution modern networks need to tackle future challenges.
For anyone interested in exploring this technology further, I recommend starting with the implementation of an MPLS VPN solution on a small topology using a network simulator like GNS3. Not only will it give you a practical understanding of how MPLS works, but it will also prepare you for real-world challenges in a complex network infrastructure.
Exploring and implementing SD-WAN technologies or other software-defined network solutions can offer additional benefits in terms of flexibility and centralized management, adapting to the dynamic requirements of client networks.
References:
Luc. De Ghein, MPLS fundamentals. Cisco Press, 2006.
Lancy. Lobo, Umesh. Lakshman, Andy. Schutz, Raymond. Zhang, and Alex. Raj, MPLS configuration on Cisco IOS software. Cisco Press, 2006.